Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive treatment used in physiotherapy to promote healing in injured tissues. It involves the application of high-energy acoustic waves to specific areas of the body. These shockwaves generate mechanical pressure and stress on tissues, which stimulates cellular activity, increases blood flow, and accelerates the healing process. This therapy is commonly used for conditions like plantar fasciitis, tendinitis, and other musculoskeletal disorders. By enhancing tissue regeneration and reducing pain, shockwave therapy helps patients recover more quickly and effectively, improving their mobility and overall function.
Shockwave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive treatment used in physiotherapy to promote healing in injured tissues. It involves the application of high-energy acoustic waves to specific areas of the body. These shockwaves generate mechanical pressure and stress on tissues, which stimulates cellular activity, increases blood flow, and accelerates the healing process. This therapy is commonly used for conditions like plantar fasciitis, tendinitis, and other musculoskeletal disorders. By enhancing tissue regeneration and reducing pain, shockwave therapy helps patients recover more quickly and effectively, improving their mobility and overall function.
From a physiotherapeutic perspective, shockwave therapy is valued for its ability to accelerate recovery and reduce pain without the need for invasive procedures or medication. Physiotherapists often incorporate shockwave therapy as part of a broader treatment plan that includes exercises, manual therapy, and other modalities. The treatment sessions are typically brief, lasting around 15-20 minutes, and are performed once a week for several weeks, depending on the severity and type of the condition. The non-invasive nature of shockwave therapy means that there is minimal downtime, allowing patients to continue with their daily activities and rehabilitation exercises with minimal interruption. This approach not only helps in managing pain but also improves the overall function and mobility of the affected areas, contributing to better long-term outcomes for patients.
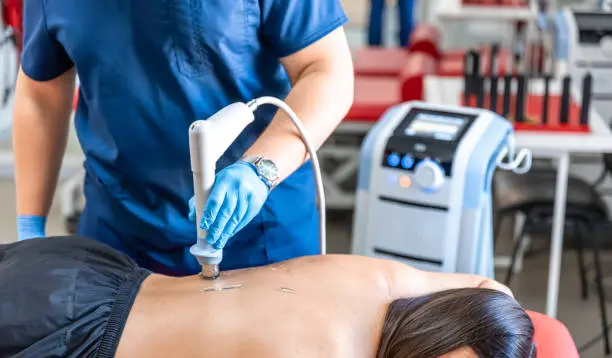
What conditions can be effectively treated with shockwave therapy in physiotherapy?
Shockwave therapy is effectively used in physiotherapy to treat a variety of musculoskeletal conditions. It is particularly beneficial for chronic tendinopathies such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinitis, and patellar tendinitis (jumper's knee). Additionally, it is used to address calcific shoulder tendinitis and lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow). This therapy helps in the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome, characterized by painful knots in muscles, and can aid in the healing of stress fractures and delayed unions of fractures. Shockwave therapy's ability to stimulate tissue regeneration and enhance blood flow makes it a valuable tool for treating these conditions, promoting faster recovery and pain relief.
Are there any side effects or risks associated with shockwave therapy?
While shockwave therapy is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, there are some potential side effects and risks associated with its use. Patients may experience mild to moderate pain or discomfort during and after the treatment session, which typically subsides within a few days. Other common side effects include swelling, redness, bruising, or hematoma at the treatment site. In rare cases, patients might develop skin irritation or damage. It is also possible to experience temporary numbness or tingling in the treated area. Although serious complications are uncommon, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as blood clotting disorders or nerve disorders, should consult with their healthcare provider before undergoing shockwave therapy to avoid adverse effects.
